The Crucial Role of Yearly Eye Exams in Diabetic Care: Why Optometrists Are Frontline Guardians
Diabetes, a chronic disease affecting millions worldwide, poses significant threats to patients’ overall health – and their vision is no exception. Diabetic eye disease, including diabetic retinopathy (DR) and diabetic macular edema (DME), are leading causes of blindness in adults. Yet, with timely detection and treatment, many of these vision losses can be prevented. This is where optometrists play a vital role in the co-management of diabetes, underscoring the importance of yearly eye exams for diabetic patients.
The Diabetes Epidemic and Its Ocular Consequences
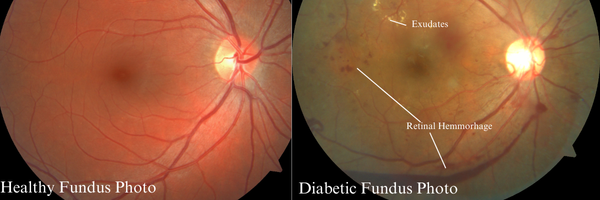
The diabetes epidemic continues to grow, with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) estimating that over 38 million Americans live with the disease. Diabetes can damage blood vessels throughout the body, including the delicate vasculature of the retina. Over time, this damage can progress to diabetic retinopathy (DR), characterized by microaneurysms, hemorrhages, and retinal edema. In advanced stages, fragile new blood vessels may grow, increasing the risk of vision-threatening complications like retinal detachment.
Diabetic macular edema (DME), a common complication of diabetic retinopathy, involves swelling of the macula, the area responsible for your detailed, central vision. This edema can cause rapid and profound vision loss if left untreated. The longer a person lives with diabetes and/or the more unstable a person’s blood sugar, the higher their risk for developing DR and DME. Early detection through yearly eye exams is critical to preserving vision in these patients.
Optometrists: The Frontline of Diabetic Eye Care
While ophthalmologists often perform the treatment for advanced diabetic eye disease, optometrists serve as the frontline in detecting these conditions. They play a crucial role in the co-management of diabetes, working collaboratively with primary care physicians and endocrinologists to ensure patients receive comprehensive care.
Yearly eye exams for diabetic patients should include a dilated retinal exam, where the doctor visually inspects the retina for signs of diabetic eye disease. Optometrists are trained to recognize early signs of DR and DME, including microaneurysms, retinal hemorrhages, and retinal edema. They can also assess a patient’s risk factors, such as their duration of diabetes, blood sugar control, and the presence of other health conditions like hypertension and kidney disease.
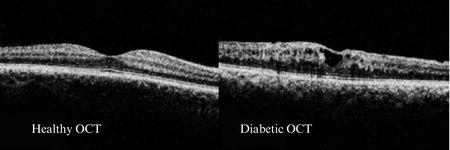
Fundus Photography and OCT: Enhancing Diabetic Eye Screening
Advances in fundus photography and optical coherence tomography (OCT) have made it easier for optometrists to screen diabetic patients for eye disease. Fundus photography involves capturing high-resolution images of the retina, which can be reviewed for signs of diabetic eye disease. These images can also be used to track changes in the retina over time, allowing for early detection of disease progression.
OCT is a non-invasive imaging technology that provides cross-sectional images of the retina. It is particularly useful in detecting DME, as it can measure retinal thickness and detect small amounts of edema. OCT can also help monitor a patient’s response to treatment for DME, allowing for adjustments to their care plan as needed.
The Importance of Patient Education and Adherence
While yearly eye exams are essential, patient education and adherence to care recommendations are equally important. Optometrists play a key role in educating diabetic patients about their risk for eye disease, the importance of blood sugar and blood pressure control, and the need for regular follow-up exams.
Conclusion
Diabetes poses a significant threat to patients’ vision, but with yearly eye exams and timely treatment, many of these vision losses can be prevented. Optometrists serve as frontline guardians of diabetic eye health, detecting disease at its earliest stages and collaborating with other healthcare providers to ensure patients receive comprehensive care. By leveraging advances in fundus photography and OCT, and through patient education and support, optometrists play a vital role in the co-management of diabetes and preserving the vision of diabetic patients.
As the diabetes epidemic continues to grow, the importance of yearly eye exams for diabetic patients cannot be overstated. Optometrists stand at the forefront of diabetic eye care, working collaboratively to detect disease, manage risk factors, and promote adherence to care recommendations. Through these efforts, they help ensure diabetic patients preserve their precious gift of sight for years to come.